About
In this code snippet, we will learn how to call the command line in C#.
We will be using a Nuget package called CliWrap which makes it easier compared to using the System.Diagnostics.Process class. But I will also show you how to use the Process class if you don’t want extra dependencies in your project. And it’s still a useful class as it can be used to run any executable (.exe file) from your C# code.
Note: Here’s the official CliWrap GitHub and documentation with a more detailed list of all the options.
Let’s have a look at the code below to see how to call the command line from C#.
Prerequisites:
Before getting started you need to install the CliWrap NuGet package into your project and add the following using statement at the top of your code file.
using CliWrap; using CliWrap.Buffered;
Calling Ping Example Code:
This first code example shows how to make a very simple call to the command line by calling ping and passing it an argument.
using CliWrap;
using CliWrap.Buffered;
namespace CliWrapTest
{
internal class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
await PingTest();
}
public static async Task PingTest()
{
string hostname = "192.168.1.1";
Console.WriteLine("Start CLI call ...");
using var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10));
var result = await Cli.Wrap("ping")
.WithArguments($"{hostname}")
.ExecuteBufferedAsync(cts.Token);
if (result.IsSuccess)
{
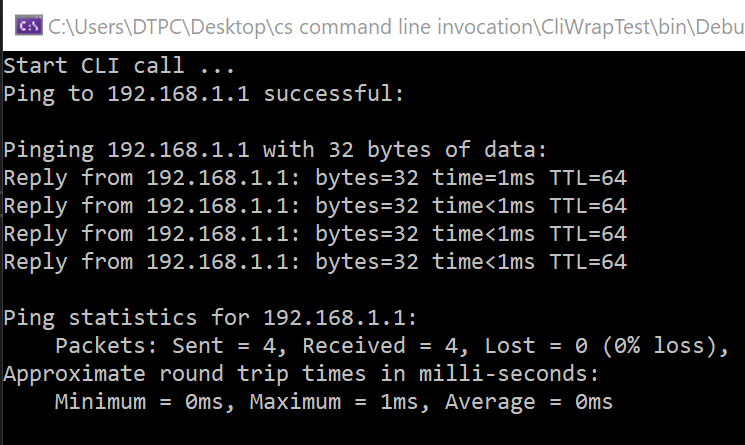
Console.WriteLine($"Ping to {hostname} successful:");
Console.WriteLine(result.StandardOutput);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Ping to {hostname} failed with exit code {result.ExitCode}:");
Console.WriteLine(result.StandardError);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
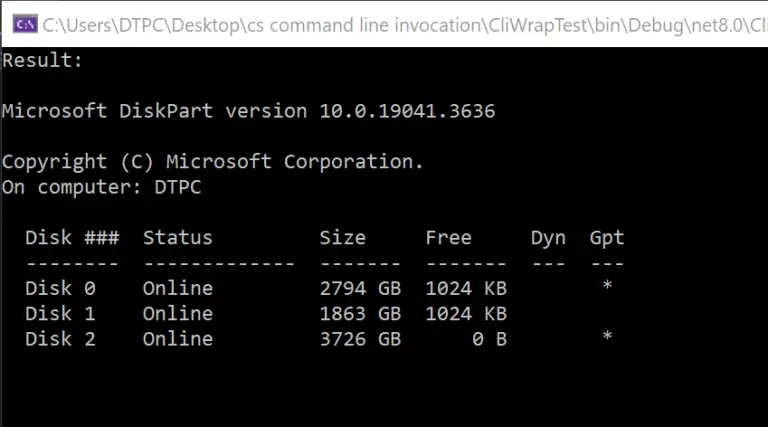
Result
Calling Diskpart Example Code:
In this example, we’ll call diskpart and pass it a script file with commands(for this example it only contains the list disk command). Additionally, I will show you how to prompt for elevated permissions as admin-level permissions are required to run diskpart.
using CliWrap;
using CliWrap.Buffered;
namespace CliWrapTest
{
internal class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
await DiskPartTest();
}
public static async Task DiskPartTest()
{
if (!IsAdministrator())
{
Console.WriteLine("Please run this application as an administrator.");
return;
}
string scriptFilePath = "C:\\Users\\DTPC\\Desktop\\cs command line invocation\\CliWrapTest\\list_disk_script.txt";
using var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10));
var result = await Cli.Wrap("diskpart")
.WithArguments($"/s \"{scriptFilePath}\"")
.ExecuteBufferedAsync(cts.Token);
if (result.ExitCode == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Result: ");
Console.WriteLine(result.StandardOutput);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: Command failed with exit code {result.ExitCode}");
Console.WriteLine(result.StandardError);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static bool IsAdministrator()
{
var identity = System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent();
var principal = new System.Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal(identity);
return principal.IsInRole(System.Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator);
}
}
}
Permission Elevation Prompt
You’ll need to add an app.manifest file into your project with the following XML. This will prompt you to elevate to the required permission.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<assembly manifestVersion="1.0" xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
<security>
<requestedPrivileges>
<requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false" />
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>
</assembly>
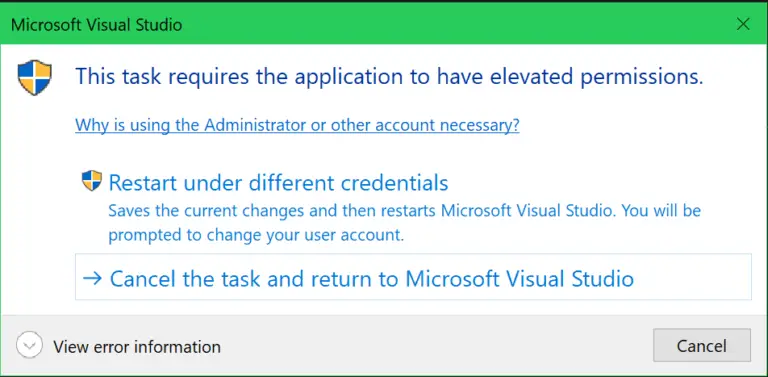
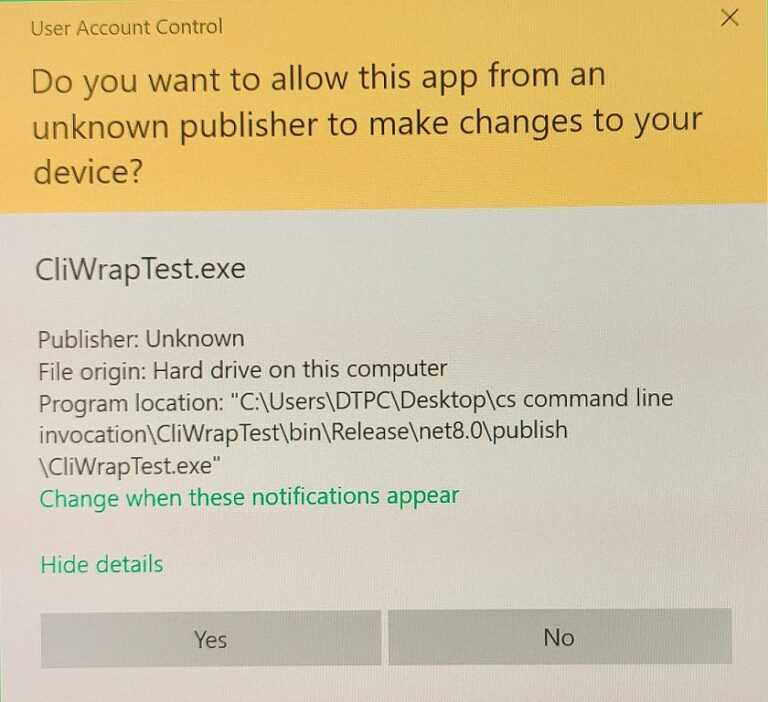
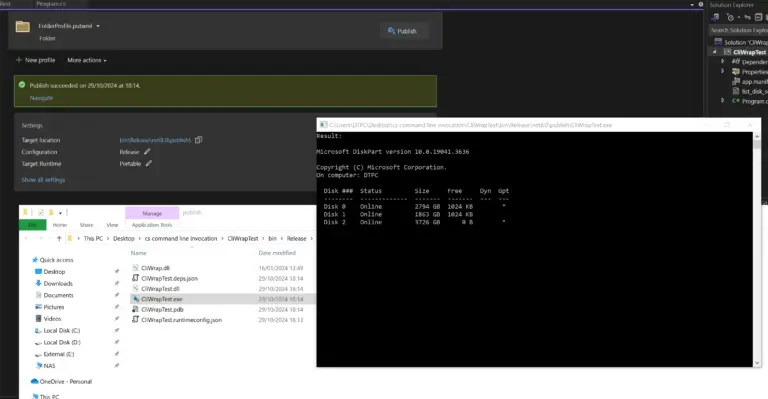
If you now run your project Visual Studio will give you this prompt. Accept it and Visual Studio will restart in admin mode.
Result
If you release/publish the app and run the executable you will get the following prompt.
Process Class Calling Diskpart Example Code:
In this final example, I will also show you how to call the command line with the Process class.
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace CliWrapTest
{
internal class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
await DiskPartWithProcess();
}
static async Task DiskPartWithProcess()
{
string scriptFilePath = "C:\\Users\\DTPC\\Desktop\\cs command line invocation\\CliWrapTest\\list_disk_script.txt";
//Create a ProcessStartInfo object.
var startInfo = new ProcessStartInfo
{
FileName = "diskpart",
Arguments = $"/s \"{scriptFilePath}\"",
UseShellExecute = false,
CreateNoWindow = true,
RedirectStandardOutput = true,
RedirectStandardError = true,
Verb = "runas" //Run with elevated privileges.
};
//Start the process.
using (var process = Process.Start(startInfo))
{
//Read the output and error.
Task<string> outputTask = process.StandardOutput.ReadToEndAsync();
Task<string> errorTask = process.StandardError.ReadToEndAsync();
//Wait for the process to exit.
process.WaitForExit();
//Results.
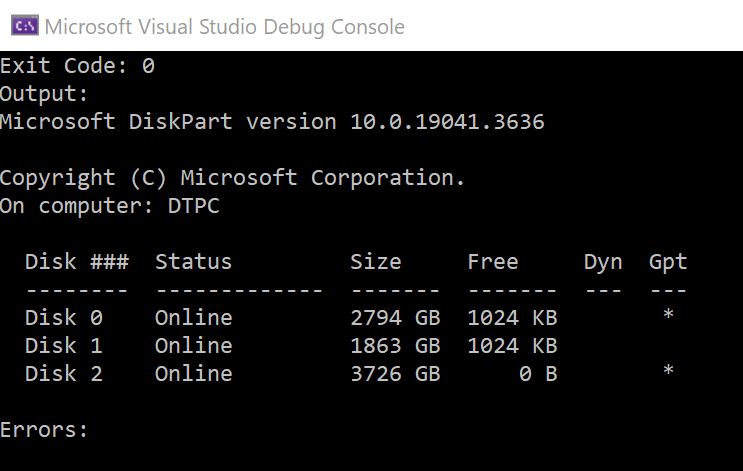
Console.WriteLine("Exit Code: " + process.ExitCode);
Console.WriteLine("Output: " + await outputTask);
Console.WriteLine("Errors: " + await errorTask);
}
}
}
}