Home

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to throw and handle an exception in PHP.
Exceptions are used to indicate that an error has occurred within our code.
For this demo, we’ll make a simple function that returns the sum of all the elements in a given array. But if the array is empty we’ll throw an exception. We’ll also check the data type of each element using gettype() to make sure the provided value is in fact a number, else an exception will be thrown.
Finally, the try catch block will be used to gracefully handle any exceptions.
Let’s see the code example below.
Code:
index.php
<?php
//Entry point////////////////////////////////////////////////
$array = [ 11, 56, 5, 8 ]; //Returns sum: 80
//$array = []; //Throws exception: Array is Empty!
//$array = [ "5", 58, 9, 23 ]; //Throws exception: A non numeric value was encountered!
try{
//Any exceptions that come up from the code executed form within this code block will be caught by the catch block below.
echo sumArray($array);
}catch(Exception $ex){
echo "En error occured: " . $ex->getMessage();
}finally{
//The code in this block will always run(exception or not).
//It can be used for cleanup(logging, closing connections, etc).
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Functions///////////////////////////////////////////////////
function sumArray($array){
//Make sure the array isn't empty.
if(count($array) <= 0)
throw new Exception("Array is Empty!");
$sum = 0;
foreach($array as $element){
//Use the gettype() function to check if for the correct data type.
if(gettype($element) != "integer" && gettype($element) != "double")
throw new Exception("A non numeric value was encountered!");
$sum += $element;
}
return $sum;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 
About
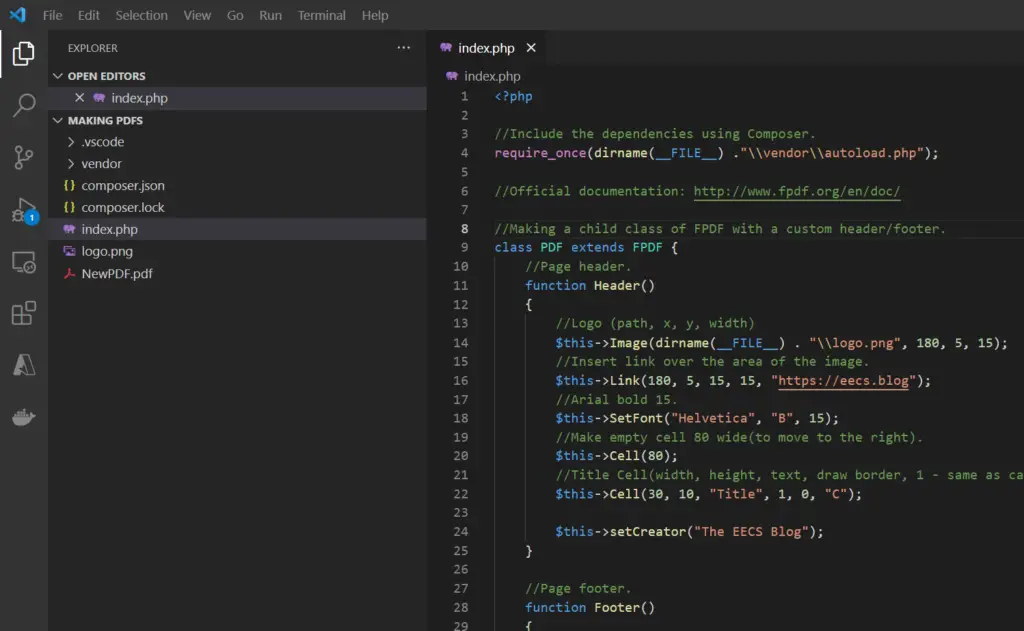
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to make a PDF file in PHP.
We will use the FPDF library to generate a PDF. More specifically we’ll see how to create page headers/footers, add page numbers, write text, use cells, use multicell, inserting links and images.
Let’s see how to do it in the example below.
Installing FPDF:
Install FPDF using Composer by opening your project directory in cmd and running this:
composer require setasign/fpdf
If you don’t know what Composer is or how to use it check out this post I made.
Code:
PDF.php
<?php
//Include the dependencies using Composer.
require_once(dirname(__FILE__) ."\\vendor\\autoload.php");
//Official documentation: http://www.fpdf.org/en/doc/
//Making a child class of FPDF with a custom header/footer.
class PDF extends FPDF {
//Page header.
function Header()
{
//Logo (path, x, y, width)
$this->Image(dirname(__FILE__) . "\\logo.png", 180, 5, 15);
//Insert link over the area of the image.
$this->Link(180, 5, 15, 15, "https://eecs.blog");
//Arial bold 15.
$this->SetFont("Helvetica", "B", 15);
//Make empty cell 80 wide(to move to the right).
$this->Cell(80);
//Title Cell(width, height, text, draw border, 1 - same as calling Ln(), center text).
$this->Cell(30, 10, "Title", 1, 0, "C");
$this->setCreator("The EECS Blog");
}
//Page footer.
function Footer()
{
//Position at 1.5 cm from bottom.
$this->SetY(-15);
//Set font.
$this->SetFont("Helvetica", "I", 8);
//Set page number. $this->PageNo() gets current page number.
$this->Cell(0, 10, "Page " . $this->PageNo() . "/{nb}", 0, 0, "C");
}
}
//Make PDF////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Instantiation PDF(child class of FPDF).
$pdf = new PDF();
//Defines an alias for the total number of pages.
$pdf->AliasNbPages();
//Add a page.
$pdf->AddPage();
//left, top, right
$pdf->SetMargins(10, 10, 10);
//Enable auto page breaks with a margin of 0.5cm.
$pdf->SetAutoPageBreak(true, 0.5);
//Font type, style(B - bold, I - italic, U - underline, "" - none), font size
$pdf->SetFont("Helvetica", 'B', 10);
//Set text color in RGB.
$pdf->SetTextColor(35, 31, 32);
//Sets background color.
$pdf->SetFillColor(145, 205, 255);
//Set "cursor" x,y position.
$pdf->SetXY(10, 30);
//Cell(width, height, text, )
$pdf->MultiCell(180, 4, "Multicell text: Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nulla eget magna tristique, dignissim enim nec, suscipit purus. Donec tellus nibh, iaculis ut aliquet ut, faucibus a elit. Sed quam dui, dictum et nisi at, dapibus auctor neque. Donec eu metus vitae augue vestibulum finibus. Maecenas condimentum dui orci, sed vestibulum dolor suscipit quis. Proin tempor imperdiet ex a finibus. Maecenas blandit viverra est, ac maximus erat efficitur a. Cras cursus eros et sapien ultrices varius.", 0);
$pdf->SetXY(10, 60);
$pdf->Cell(30,5, "Some text.", 0);
$pdf->SetXY(10, 70);
$pdf->Cell(30,5, "Some text.", 0);
$pdf->SetXY(10, 80);
$pdf->Cell(30,5, "Some text.", 0);
//Ln() can be used to move the "cursor" down instead of setting the x,y every time.
$pdf->Ln(10);
$pdf->Cell(30,5, "Some text.", 0);
$pdf->Ln(10);
//Degree symbol conversion.
$pdf->Cell(30,5, "Temperature: 25" . iconv('UTF-8', 'windows-1252', '°C'), 0);
$pdf->Ln(10);
//Text() or Write() can also be used to write text insated of Cell().
$pdf->Text(10, 120, "Some other text.");
$pdf->Ln(10);
$pdf->Write(10, "Some other text.");
//Write file as:
//I: send the file inline to the browser. The PDF viewer is used if available.
//D: send to the browser and force a file download with the name given by name.
//F: save to a local file with the name given by name (may include a path).
//S: return the document as a string.
//Write the PDF file. Output(destination, "path")
$pdf->Output('F', dirname(__FILE__) . "\\NewPDF.pdf");
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to read and write excel files in PHP.
We will use the PHPSpreadsheet library to read/write Excel files and we’ll learn how to read cells, find a specific string in a row or column, write to cells, set cell styling and formatting(like setting the border, background color, etc) and we’ll see how to insert images.
Let’s see how to do it in the example below.
Installing PHPSpreadsheet:
Install PHPSpreadsheet using Composer by opening your project directory in cmd and running this:
composer require phpoffice/phpspreadsheet
If you don’t know what Composer is or how to use it check out this post I made.
Note:
You might have to enable the gd PHP extension for this to work. I first got this error:
Problem 1
– Root composer.json requires phpoffice/phpspreadsheet ^1.18 -> satisfiable by phpoffice/phpspreadsheet[1.18.0].
– phpoffice/phpspreadsheet 1.18.0 requires ext-gd * -> it is missing from your system. Install or enable PHP’s gd extension.
FIX: If you are using XAMPP like I am open up your php.ini file and add this: extension=gd to the bottom of it. Then save the file and restart the Apache webserver and try to install the package again.
Reading Excel Files Code:
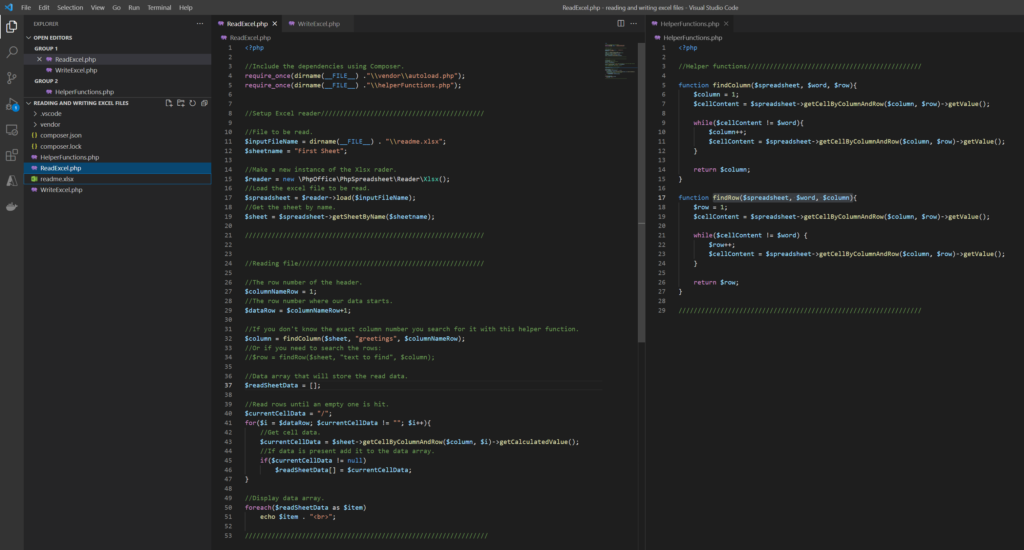
ReadExcel.php
<?php
//Include the dependencies using Composer.
require_once(dirname(__FILE__) ."\\vendor\\autoload.php");
require_once(dirname(__FILE__) ."\\helperFunctions.php");
//Setup Excel reader///////////////////////////////////////////
//File to be read.
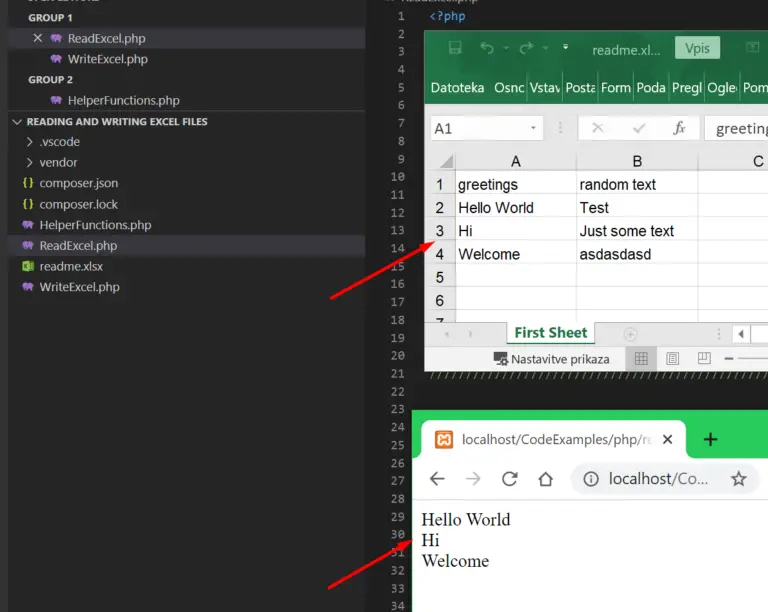
$inputFileName = dirname(__FILE__) . "\\readme.xlsx";
$sheetname = "First Sheet";
//Make a new instance of the Xlsx rader.
$reader = new \PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Reader\Xlsx();
//Load the excel file to be read.
$spreadsheet = $reader->load($inputFileName);
//Get the sheet by name.
$sheet = $spreadsheet->getSheetByName($sheetname);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Reading file/////////////////////////////////////////////////
//The row number of the header.
$columnNameRow = 1;
//The row number where our data starts.
$dataRow = $columnNameRow+1;
//If you don't know the exact column number you search for it with this helper function.
$column = findColumn($sheet, "greetings", $columnNameRow);
//Or if you need to search the rows:
//$row = findRow($sheet, "text to find", $column);
//Data array that will store the read data.
$readSheetData = [];
//Read rows until an empty one is hit.
$currentCellData = "/";
for($i = $dataRow; $currentCellData != ""; $i++){
//Get cell data.
$currentCellData = $sheet->getCellByColumnAndRow($column, $i)->getCalculatedValue();
//If data is present add it to the data array.
if($currentCellData != null)
$readSheetData[] = $currentCellData;
}
//Display data array.
foreach($readSheetData as $item)
echo $item . "<br>";
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// HelperFunctions.php
<?php
//Helper functions//////////////////////////////////////////////
function findColumn($spreadsheet, $word, $row){
$column = 1;
$cellContent = $spreadsheet->getCellByColumnAndRow($column, $row)->getValue();
while($cellContent != $word){
$column++;
$cellContent = $spreadsheet->getCellByColumnAndRow($column, $row)->getValue();
}
return $column;
}
function findRow($spreadsheet, $word, $column){
$row = 1;
$cellContent = $spreadsheet->getCellByColumnAndRow($column, $row)->getValue();
while($cellContent != $word) {
$row++;
$cellContent = $spreadsheet->getCellByColumnAndRow($column, $row)->getValue();
}
return $row;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting Output:
Writing Excel Files Code:
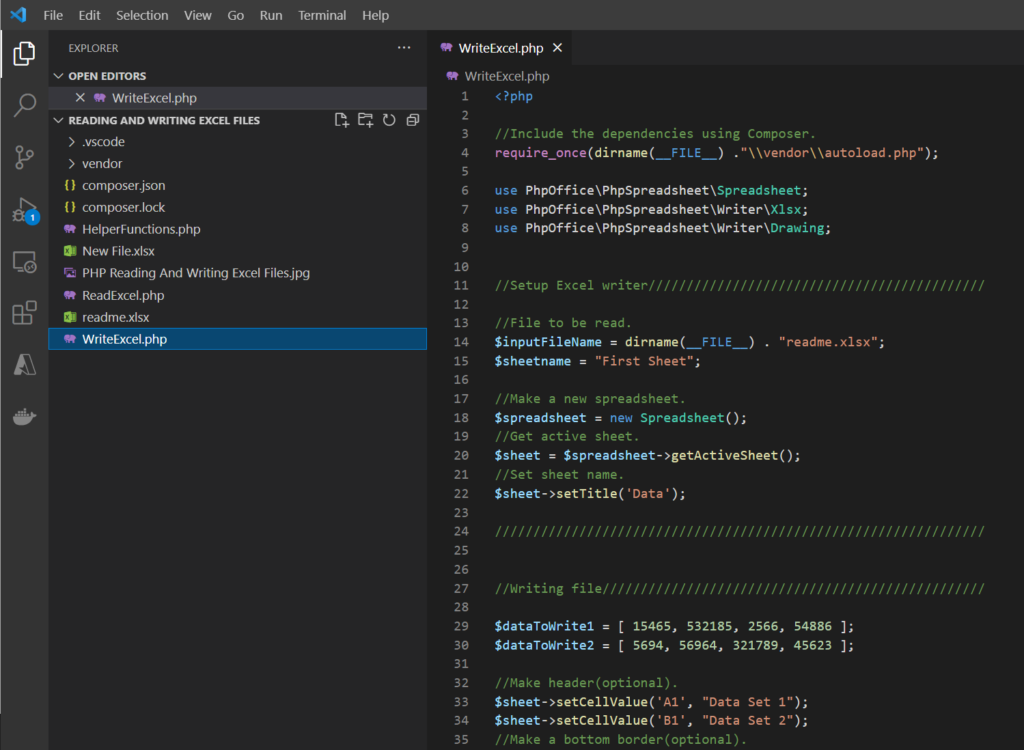
WriteExcel.php
<?php
//Include the dependencies using Composer.
require_once(dirname(__FILE__) ."\\vendor\\autoload.php");
use PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Spreadsheet;
use PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Writer\Xlsx;
use PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Writer\Drawing;
//Setup Excel writer////////////////////////////////////////////
//File to be read.
$inputFileName = dirname(__FILE__) . "readme.xlsx";
$sheetname = "First Sheet";
//Make a new spreadsheet.
$spreadsheet = new Spreadsheet();
//Get active sheet.
$sheet = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet();
//Set sheet name.
$sheet->setTitle('Data');
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
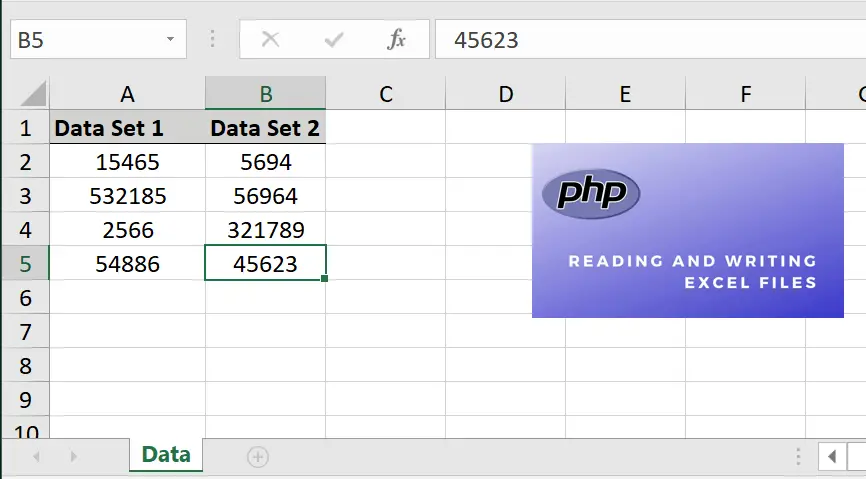
//Writing file//////////////////////////////////////////////////
$dataToWrite1 = [ 15465, 532185, 2566, 54886 ];
$dataToWrite2 = [ 5694, 56964, 321789, 45623 ];
//Make header(optional).
$sheet->setCellValue('A1', "Data Set 1");
$sheet->setCellValue('B1', "Data Set 2");
//Make a bottom border(optional).
$sheet->getStyle('A1:B1')->getBorders()->getBottom()->setBorderStyle(\PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Style\Border::BORDER_THIN);
//Set header background color(optional).
$sheet->getStyle('A1:B1')->getFill()->setFillType(\PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Style\Fill::FILL_SOLID)->getStartColor()->setRGB('d2d3d1');
//Set text bold.
$sheet->getStyle("A1:B1")->getFont()->setBold(true);
//Set auto resize(optional).
$sheet->getColumnDimension('A')->setAutoSize(true);
//For more styling/formatting info. check out the official documentation: https://phpspreadsheet.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
//Write data 1.
$i = 2;
foreach($dataToWrite1 as $item){
//Write value into cell.
$sheet->setCellValue('A'.$i, $item);
//Set cell alignment(optional).
$sheet->getStyle('A'.$i)->getAlignment()->setHorizontal(\PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Style\Alignment::HORIZONTAL_CENTER);
$i++;
}
//Write data 2.
$i = 2;
foreach($dataToWrite2 as $item){
//Write value into cell.
$sheet->setCellValue('B'.$i, $item);
//Set cell alignment(optional).
$sheet->getStyle('B'.$i)->getAlignment()->setHorizontal(\PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Style\Alignment::HORIZONTAL_CENTER);
$i++;
}
//Adding an image.
//Create drawing.
$objDrawing = new \PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Worksheet\MemoryDrawing();
//Get image path.
$imgPathName = dirname(__FILE__) . "\\PHP Reading And Writing Excel Files.jpg";
//Create gdImage from image.
$gdImage = imagecreatefromjpeg($imgPathName);
//Set gdImage as a property to drawing.
$objDrawing->setImageResource($gdImage);
//Set drawing properties.
$objDrawing->setName('Thumbnail');
$objDrawing->setDescription('PHP Reading And Writing Excel Files');
//Set file type.
$objDrawing->setRenderingFunction(\PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Worksheet\MemoryDrawing::RENDERING_JPEG);
$objDrawing->setMimeType(\PhpOffice\PhpSpreadsheet\Worksheet\MemoryDrawing::MIMETYPE_DEFAULT);
//Set position.
$objDrawing->setCoordinates('D1');
//Set position offset.
$objDrawing->setOffsetX(50);
$objDrawing->setOffsetY(50);
//Set width and height.
$objDrawing->setWidth(400);
$objDrawing->setHeight(100);
$objDrawing->setWorksheet($sheet);
//Write excel file.
$savePath = dirname(__FILE__);
$writer = new Xlsx($spreadsheet);
$writer->save($savePath . "\\New File.xlsx");
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll see how to work with HTML using DomDocument in PHP.
If you need to change HTML in code or extract some data from it(web scraping) you can use the DomDocuemnt class to help you with that. You simply create a new instance of it and load the HTML and then you can use its functions to access the DOM.
Official DomDocument documentation here.
Let’s see the example below.
Code:
index.php
<?php
//For this demo I just made an HTML string.
//But you could read it from an .html file or get the it from a webpage with file_get_contents().
$html = "
<div id='wrapperDiv'>
<div id='test' class='contentDiv'>
<h2>Paragraph</h2>
<p class='text'>Some text</p>
</div>
<div class='contentDiv'>
<h2>List</h2>
<ul id='FirstListOfItems' class='itemList'>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
";
//Make DomDocument from HTML/////////////////////////////
//Make a new DomDocument object.
$dom = new DomDocument;
//Load the html into the object.
$dom->loadHTML($html);
//Discard white space.
$dom->preserveWhiteSpace = false;
//Get the element by id. ///////////////////////////////
$list = $dom->getElementById("FirstListOfItems");
//Get its children.
$listItems = $list->childNodes;
//Iterate over all the <li> children elements and print their values.
foreach($listItems as $item)
echo $item->nodeValue . " ";
echo "<br>";
//Make XPath from DomDocument.//////////////////////////
$xpath = new DOMXPath($dom);
//We can use xpath->query() to get elements aswell.
$paragraph = $xpath->query("//*[@id='wrapperDiv']/div/p");
//getAttribute() can get any attribute value(class in this case).
echo "Get class attribute: " . $paragraph->item(0)->getAttribute('class');
echo "<br>";
//Get elements by class with xpath./////////////////////
$contentDivs = $xpath->query("//*[@class='contentDiv']");
//List content in all divs.
foreach($contentDivs as $contentDiv)
echo $contentDiv->nodeValue;
echo "<br>";
//Get elements by tag and replace their value.//////////
$titles = $dom->getElementsByTagName("h2");
//For this example lets replace the text.
foreach($titles as $title)
$title->nodeValue = "New Title";
//Creating a new element.///////////////////////////////
//Get list.
$parent = $dom->getElementById("FirstListOfItems");
//Create a new element.
$newElement = $dom->createDocumentFragment();
//Add content.
$newElement->appendXML('<li>Item 4</li>');
//Append the new element to the existing list.
$parent->appendChild($newElement);
//Print out the whole DOM.//////////////////////////////
//Get and print the DomDocument data.
echo $dom->saveHTML(); Resulting Output:

About
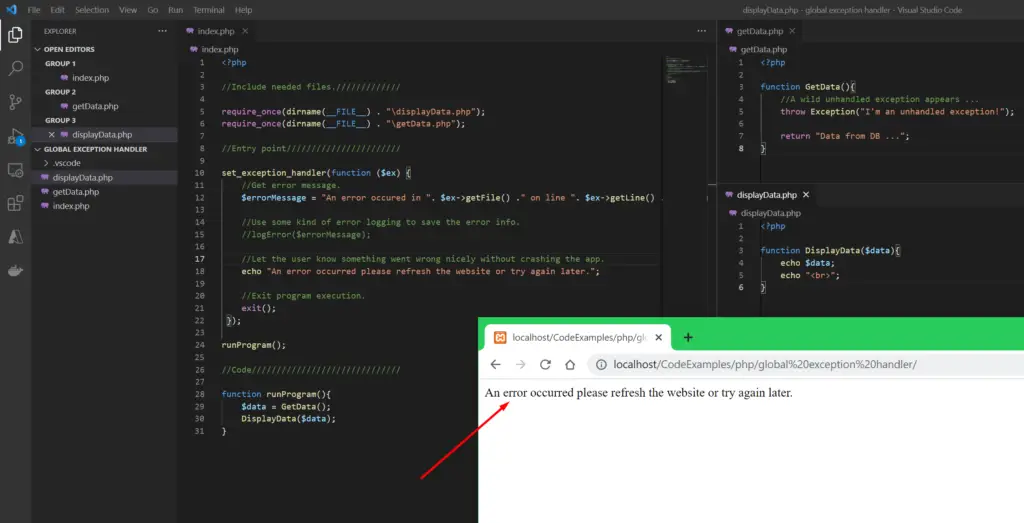
In this code snippet, we’ll make a global exception handler in PHP.
A global exception handler is used to catch any unhandled exception that might bubble up in your code. This way you can log the exception and let the user know there was an error instead of the program just crashing.
Let’s see how to implement it in the example below.
Code:
index.php
<?php
//Include needed files./////////////
require_once(dirname(__FILE__) . "\displayData.php");
require_once(dirname(__FILE__) . "\getData.php");
//Entry point///////////////////////
set_exception_handler(function ($ex) {
//Get error message.
$errorMessage = "An error occured in ". $ex->getFile() ." on line ". $ex->getLine() ." Error message: ". $ex->getMessage();
//Use some kind of error logging to save the error info.
//logError($errorMessage);
//Let the user know something went worong nicely without crashing the app.
echo "An error occurred please refresh the website or try again later.";
//Exit program execution.
exit();
});
runProgram();
//Code//////////////////////////////
function runProgram(){
$data = GetData();
DisplayData($data);
} getData.php
<?php
function GetData(){
//A wild unhandled exception appears ...
throw Exception("I'm an unhandled exception!");
return "Data from DB ...";
} displayData.php
<?php
function DisplayData($data){
echo $data;
echo "<br>";
} Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll make a REST API with the Slim framework in PHP.
Slim is a framework that enables you to easily and quickly build REST APIs in PHP. I will show you how to make a POST and GET endpoint. Other types of requests follow the same logic. Official dodumentation here. We will also enable CORS so you can call the API from the browser.
Let’s see the example below.
Installing Slim:
Install Slim using Composer by opening your project directory in cmd and running this:
composer require slim/slim:^4.8
followed by this:
composer require slim/psr7
If you don’t know what Composer is or how to use it check out this post I made.
Code:
<?php
//Include needed files///////////////////////////////////////////
use Psr\Http\Message\ResponseInterface as Response;
use Psr\Http\Message\ServerRequestInterface as Request;
use Slim\Factory\AppFactory;
require __DIR__ . '\vendor\autoload.php';
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Setup API//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Create the API instance.
$app = AppFactory::create();
//Get the current script path and set it as base path for Slim API.
$app->setBasePath($_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME']);
//Any errors that occour will be handled and nicely displayed by Slim.
$app->addErrorMiddleware(true, true, true);
//With slim v4 you need to add this to be able to get the POST body with getParsedBody(). Else it will be null.
$app->addBodyParsingMiddleware();
//Variables.
$apiKey = "mysupersecurekey";
//CORS Enable//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Enabling CORS allows you to make requests to this API from a web browser.
$app->options('/{routes:.+}', function ($request, $response, $args) {
return $response;
});
$app->add(function ($request, $handler) {
$response = $handler->handle($request);
return $response
->withHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*') //Set a specific url where you want to enable cors. If left like so CORS will be enabled for all domains.
->withHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Origin, Authorization')
->withHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, OPTIONS');
});
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Add endpoints////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Simple GET request endpoint.
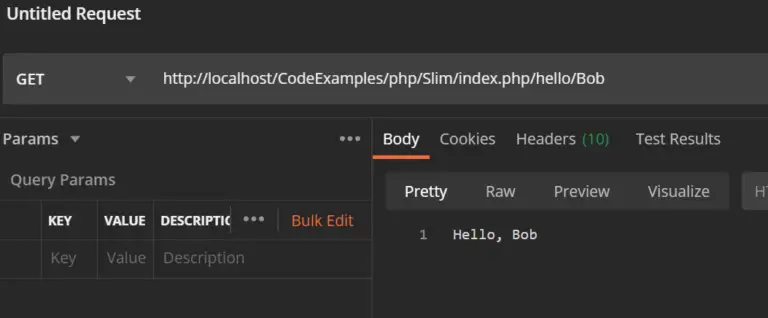
$app->get('/hello/{name}', function (Request $request, Response $response, array $args) {
$name = $args['name'];
$response->getBody()->write("Hello, $name");
return $response;
});
//POST request endpoint that takes in and returns json.
//When you make the endpoint you can pass in variables with use().
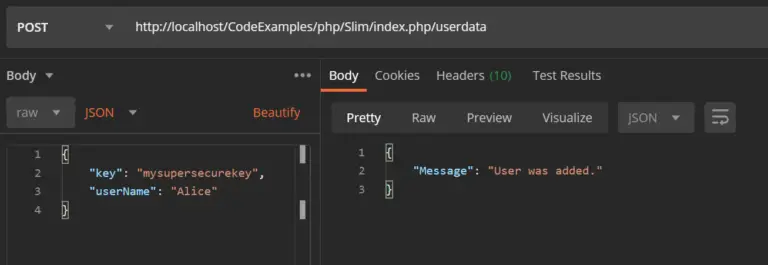
$app->post('/userdata', function ($request, $response, $args) use($apiKey){
//Get JSON from the body of the request.///////////////////////////////////////////
$requestJSON = $request->getParsedBody();
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Check if the api key is present and correct./////////////////////////////////////
if(!array_key_exists("key", $requestJSON)){
$responseBody = array('message' => 'Missing API key.');
return $response->withHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*')
->withHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST, OPTIONS")
->withJson($responseBody, 400);
}
if($apiKey != $requestJSON["key"]){
$responseBody = array('message' => 'Invalid API key.');
return $response->withHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*')
->withHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST, OPTIONS")
->withJson($responseBody, 400);
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Buisness logic here ...
//Lets pretend to add the user to the DB...
//Make a response.
$responseData = "{ \"Message\" : \"User was added.\"}";
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Return response//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Add response data.
$response->getBody()->write($responseData);
//Add headers and return the response.
return $response->withHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
});
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Add '/{routes:.+}' as last route. (Part of enabling CORS)
$app->map(['GET', 'POST', 'PUT', 'DELETE', 'PATCH'], '/{routes:.+}', function ($request, $response) {
throw new HttpNotFoundException($request);
});
//Run the API instance.
$app->run();
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll take a look at objects and basic of object oriented programming in PHP.
I will just show how to make and use classes, interfaces, properties, … in PHP. I won’t go into OOP too much as I already did some other posts about that.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
//Code/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Interface implementation in PHP.
interface IDrivable{
public function drive($destination);
}
//Abstract class implementation in PHP.
abstract class Vehicle {
//Force child class to make it's own implementation of this function.
abstract protected function FillUpTank($fuel);
//Child class will inherit this function and properties.
//Properties.
public $Mileage;
public $Year;
public $Model;
public function GetCarStats(){
echo "Mileage: " . $this->Mileage . " Year: " . $this->Year . " Model: " . $this->Model;
}
}
//Class implementation in PHP.
class Car extends Vehicle implements IDrivable{
//Constructor
function __construct($mileage, $year, $model){
//When referencing class mambers inside their class $this-> must be put infront.
$this->Mileage = $mileage;
$this->Year = $year;
$this->Model = $model;
}
public $Fuel;
//Implement FillUpTank from Vehicle.
function FillUpTank($fuel){
$this->Fuel += $fuel;
}
//Implement drive() from IDrivable interface.
public function drive($destination){
echo "Driving to " . $destination;
}
//Static class members don't need the class to be instantiated to be used.
public static $VehicleType = "road vehicle";
public static function GetVehicleType(){
return Car::$VehicleType;
}
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Entry point/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//More about OOP in PHP: https://www.php.net/manual/en/language.oop5.php
echo Car::GetVehicleType();//:: is used to access static class members.
echo "<br>";
//Make new instance of Car.
$car = new Car(100000, 2010, "Some model...");
echo $car->Model;
echo "<br>";
$car->drive("somewhere...");
echo "<br>";
$car->GetCarStats();
echo "<br>";
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting Output:

About
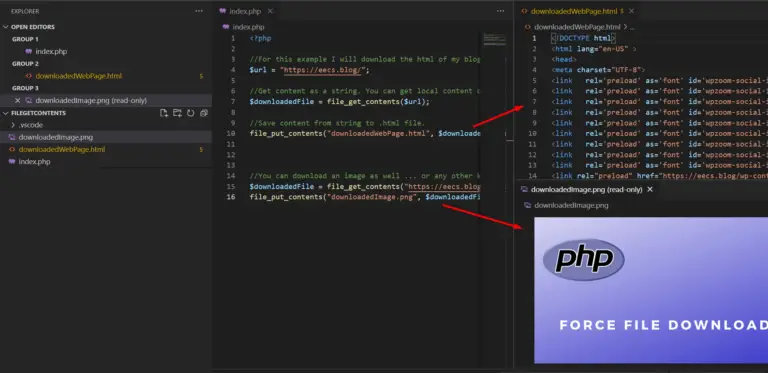
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to perform file downloads in PHP with the file_get_contents() function.
The file_get_contents() function gets/downloads a file(locally or from the web) as a string. We can then modify the string and save it with file_put_contents().
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
//For this example I will download the html of my blogs homepage.
$url = "https://eecs.blog/";
//Get content as a string. You can get local content or download it from the web.
$downloadedFile = file_get_contents($url);
//Save content from string to .html file.
file_put_contents("downloadedWebPage.html", $downloadedFile);
//You can download an image as well ... or any other kind of file.
$downloadedFile = file_get_contents("https://eecs.blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Code-Snippets-Force-File-Download-1024x576.png");
file_put_contents("downloadedImage.png", $downloadedFile); Resulting Output:

About
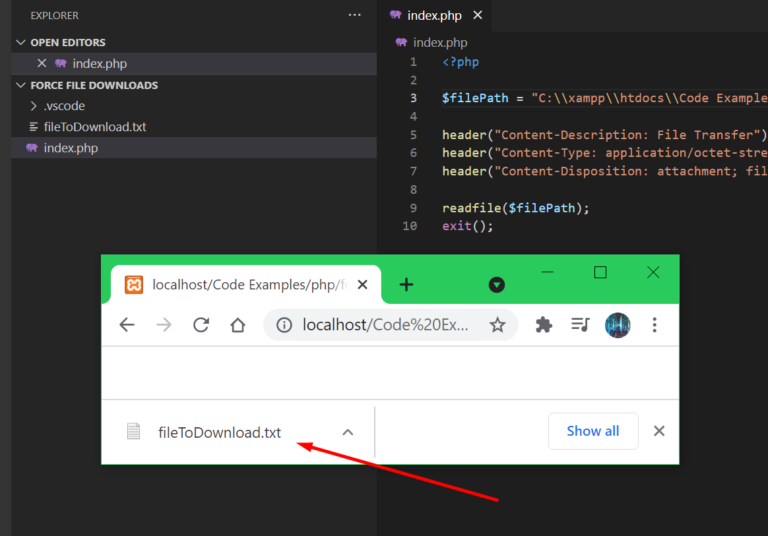
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to force file downloads in PHP.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
$filePath = "C:\\xampp\\htdocs\\Code Examples\\php\\force file downloads\\fileToDownload.txt";
header("Content-Description: File Transfer");
header("Content-Type: application/octet-stream");
header("Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=\"". basename($filePath) ."\"");
readfile($filePath);
exit(); Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to perform data validation in PHP.
Data validation is used to make sure the input data is present and in the correct format for further processing. This can be performed either on the front or backend.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
//Make sure the correct HTTP request method is used.
if($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] != "GET")
die("Wrong HTTp method used!");
//Make sure parameter is present.
if(empty($_GET["userID"]))
die("userID paremeter is missing!");
//Make sure the parameter isn't too long.
if(strlen($_GET["userID"]) > 10)
die("Paremeter value too long!");
//Sanatize string. Depending on your needs you can use differnt filters: https://eecs.blog/php-string-sanitization/
$userID = filter_var($_GET["userID"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
//Display value.
echo $userID;
//Now the $userID can be used to get user info from the data base.
//Do DB stuff ...