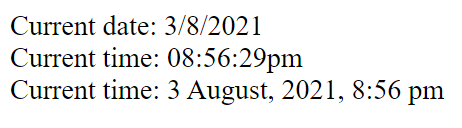Home

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn about the date() function in PHP.
The date() function takes in a string that specifies the date/time format and gives you the result.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
//Get current date as day / month / year.
echo "Current date: " . date("j/n/Y");
echo "<br>";
//Get current time as hours : minutes : seconds.
echo "Current time: " . date("h:i:sa");
echo "<br>";
//Get current date and time as day month(as short string) , year, hours : minutes (12h am/pm).
echo "Current time: " . date("j F, Y, g:i a");
echo "<br>"; Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn about the dirname() function in PHP.
The dirname() function takes in a path string and gives you the parent directory of it. A second parameter can be added where you can specify how many levels up you want to go.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php //__FILE__ contains the path of the current file. $filePath = __FILE__; echo "Current file path: " . $filePath; echo "<br>"; //Gets the path of the parent directory. echo "Parent dir. file path: " . dirname($filePath); echo "<br>"; //You can use the last parameter to specify how many levels up you want to go. echo "Parent of parent dir. file path: " . dirname($filePath, 2); echo "<br>";
Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to get HTTP request variables in PHP.
When an HTTP request is made to the PHP backend the data associated with the request(POST data, GET url parameters, cookies, …) will get stored as superglobal variables available from everywhere in the code. Here we’ll see how to access some of these values.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
//POST//////////////////////////////////
//For the following form ...
//<form>
// <input type="text" name="myvar">
// <input type = "submit" />
//</form>
// ... you can get the form data from POST request like so:
$myVar = $_POST["myvar"];
//If you are sending some data like json in the body of the POST reqeust you can get it like so:
$postBodyData = file_get_contents('php://input');
////////////////////////////////////////
//GET///////////////////////////////////
//Get url parameters from GET request.
//Example url: http://localhost/Code%20Examples/php/request%20variables/?myvar=Hello&mysecondvar=World
$myVar = $_GET["myvar"]; //value: "Hello"
$mySecondVar = $_GET["mysecondvar"]; //value: "World"
////////////////////////////////////////
//Cookies///////////////////////////////
//Get any cookies sent with the request by their name.
$cookie = $_COOKIE["mycookie"];
//////////////////////////////////////// 
About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to pass and work with variables by reference in PHP.
Variables can be passed either by value or by reference.
Usually, we do it by value meaning you pass just the value and not the variable itself. So, any changes made locally inside the function scope won’t be seen outside of the function scope.
Meanwhile, if we pass a variable as a reference is essentially like passing in the variable itself. Any changes made locally inside the function to the variable will occur outside of the function scope as well.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
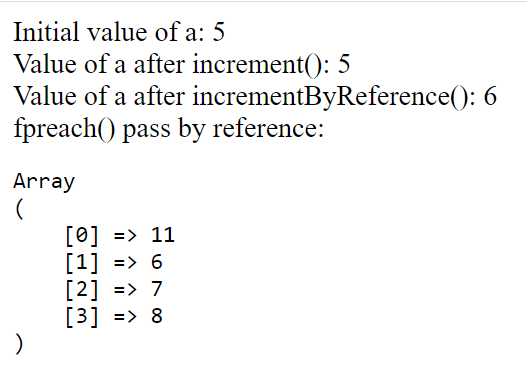
$a = 5;
echo "Initial value of a: " . $a;
echo "<br>";
//Pass by value/////////////////////////////////
increment($a);
echo "Value of a after increment(): " . $a;
echo "<br>";
////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Pass by reference/////////////////////////////
incrementByReference($a);
echo "Value of a after incrementByReference(): " . $a;
echo "<br>";
//Passing by reference works the same way with the foreach() loop.
$numbers = [ 10, 5, 6, 7 ];
foreach($numbers as &$number)
$number++;
echo "foreach() pass by reference: ";
echo "<pre>";
print_r($numbers);
echo "</pre>";
////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Functions////////////////////////////////
function increment($a){
//Here just the value gets passed and a local version of $a gets created.
$a++;
}
//Use & to make a reference parameter.
function incrementByReference(&$a){
//Here the actual variable is passed as the parameter.
//So any changes made to it in this fucntion will be reflected outside of it.
$a++;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to work with strings in PHP.
More specifically we’ll learn how to concatenate(join) strings, trim white spaces, make a string lower or upper case, get its length, check if it contains a substring and get its position, replace a substring, remove tags and slashes, split a string into an array on a specific character and join a string array back into a string.
Note: I covered just the string functions I found myself using the most. Here is the full list of string functions.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
<?php
//Concatenate strings with the . operator.
$myString = "Hello" . "" . "World! ";
//Trims whitespace.
echo "String length: " . trim($myString);
echo "<br>";
//Makes string lowercase.
echo "String to lower case: " . strtolower($myString);
echo "<br>";
//Makes string uppercase.
echo "String to upper case: " . strtoupper($myString);
echo "<br>";
//Get string length.
echo "String length: " . strlen($myString);
echo "<br>";
//Checks if a string contains a substring.
echo "Contains 'World': " . str_contains($myString, "World");
echo "<br>";
//Gets position of the first substring.
echo "Position of 'World': " . stripos($myString, "World");
echo "<br>";
//Replace substring.
echo "Replace 'Hello': " . str_replace("Hello", "Goodbye", $myString);
echo "<br>";
//Removes slashes from string.
echo "Strip slashes: " . stripslashes("File\Name.txt");
echo "<br>";
//Removes tags from string.
echo "Remove tags: " . strip_tags("<h1>Hello World!</h1>");
echo "<br>";
//Split string into an array of strigs on a certain character.
$charArray = explode(" ", $myString);
echo "Explode: ";
echo "<pre>";
print_r($charArray);
echo "</pre>";
echo "<br>";
//Makes string from a string array.
echo "Implode: " . implode($charArray); Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to work with arrays in PHP.
More specifically we’ll learn how to merge arrays, add/remove elements, reverse the array, remove duplicates, search the array, find its length, make associative arrays and get their keys. Associative arrays are use strings for indexes instead of numbers.
Note: I covered just the array functions I found myself using the most. Here is the full list of array functions.
Let’s see the code example below.
Code:
<?php
//1. way to make an array in PHP.
$numbers = array( 1, 1, 2 );
//2. way to make an array.
$numbers2 = [ 4, 5, 6 ];
//Add element to the end of an array.
array_push($numbers, 3);
echo "Add element:";
printArray($numbers);
//Remove an element from the end of an array.
array_pop($numbers2);
echo "Remove element:";
printArray($numbers2);
//Get the number of elements in the array.
echo "Number of elements:";
echo count($numbers);
echo "<br>";
//Merge arrays.
$allNumbers = array_merge($numbers, $numbers2);
echo "Merge arrays:";
printArray($allNumbers);
//Reverse the array.
array_reverse($allNumbers);
echo "Reverse array:";
printArray($allNumbers);
//Remove duplicates in an array.
$allNumbers = array_unique($allNumbers);
echo "Remove duplicates:";
printArray($allNumbers);
//Search array for element and return its index.
echo "Index of number 4:";
echo array_search(4, $allNumbers);
//Make an associative array with key value pairs.
$keyValuePairs = [ "Bob" => "15258", "Alice" => "15892" ];
//List the keys of an array.
echo "List array keys:";
printArray(array_keys($keyValuePairs));
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Prints array so we can see what is inside it..
function printArray($arr){
echo "<pre>";
print_r($arr);
echo "</pre>";
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to work with JSON in PHP.
You can use json_encode() to serialize and json_decode() to deserialize JSON. json_decode() also takes a second parameter(true/false) where you can specify if you want the JSON to be deserialized to an associative array or to an object.
In this post, you can see a practical example of JSON serialization/deserialization.
Let’s see the example code below.
Code:
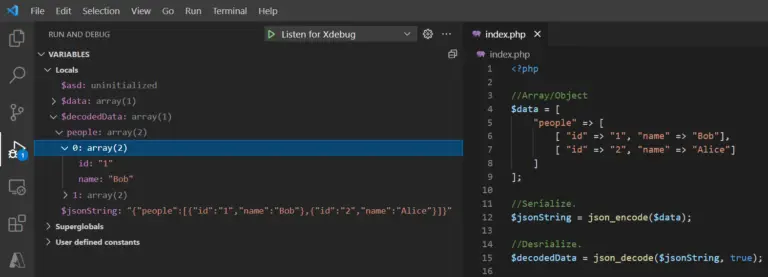
<?php
//Array/Object
$data = [
"people" => [
[ "id" => "1", "name" => "Bob"],
[ "id" => "2", "name" => "Alice"]
]
];
//Serialize.
$jsonString = json_encode($data);
//Deserialize.
$decodedData = json_decode($jsonString, true); Resulting Output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll see how to send HTTP requests with curl in PHP.
Curl can be used to make HTTP request from the backend in PHP. In this desmonstration we’ll make a POST request to a test API.
Note: Curl documentation here.
Let’s see the example below.
Code:
<?php
//Set url.
$url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts";
//Make
$requestDataObject = [ "title" => "foo", "body" => "bar", "userId" => 1 ];
//Serialize object to json.
$data = json_encode($requestDataObject);
//Initialize curl.
$curl = curl_init($url);
//Setting method type(POST, GET, ...).
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST, "POST");
//If PSOT type you can set the body data like this:
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $data);
//If request is successful return the response instead of "true".
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
//Add headers.
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array(
'Content-Type: application/json',
'Content-Length: ' . strlen($data))
);
//Make the request.
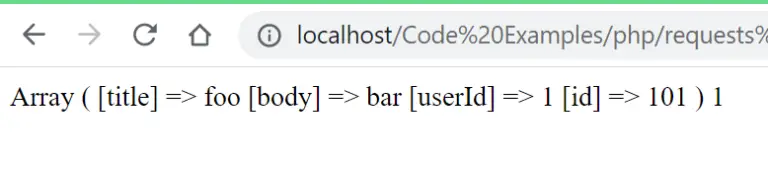
$response = curl_exec($curl);
//In this case the response will be a json string so we'll use json_decode() to deserialize it.
$jsonResponse = json_decode($response, true);
//Show response.
echo print_r($jsonResponse); Resulting output:

About
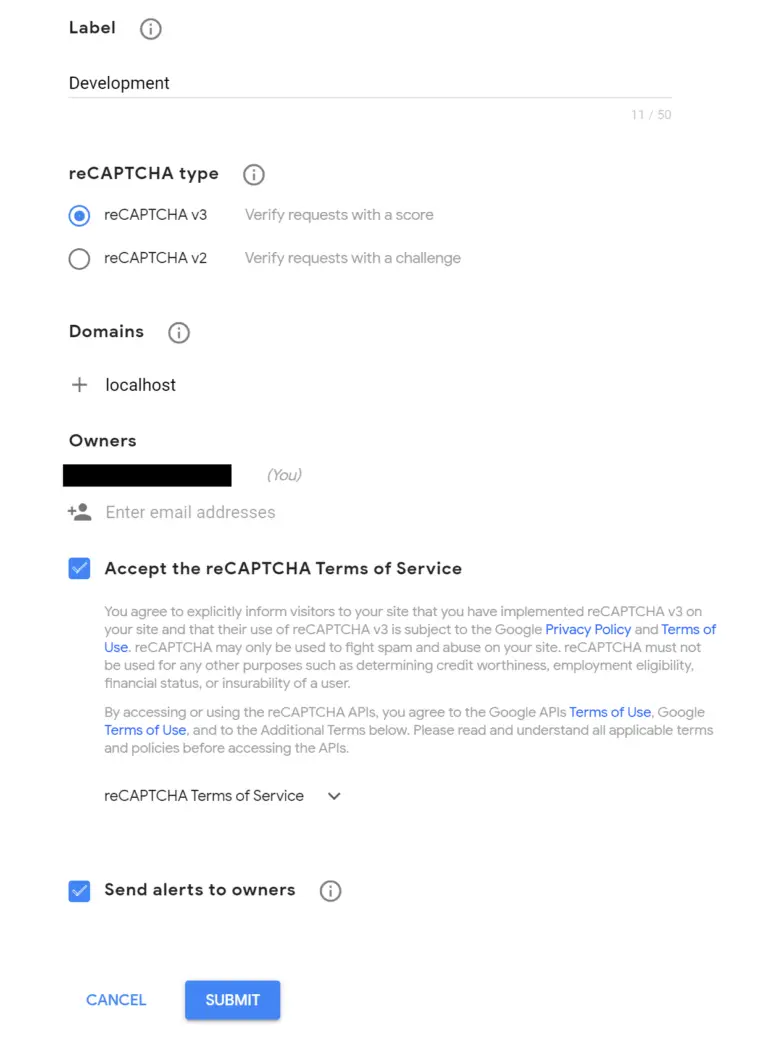
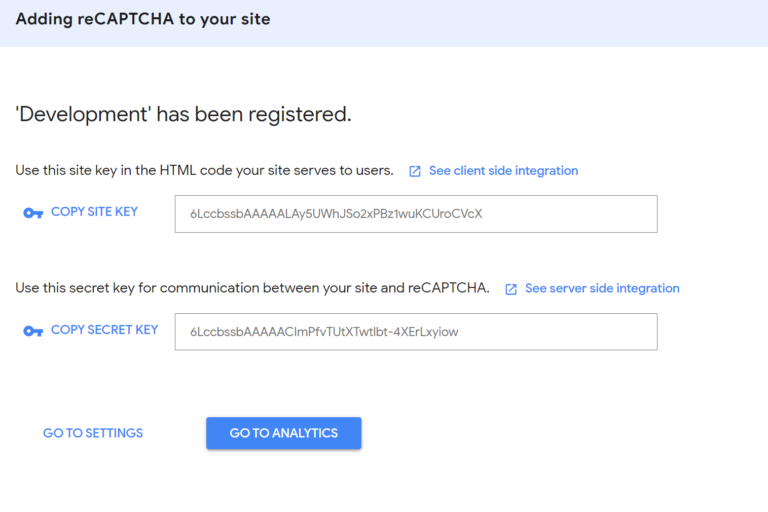
In this post, we’ll learn how to implement reCAPTCHA on a website.
Recaptcha is used to confirm that the user interaction on your site was made by a human and not by some script. For example, if you have a contact form on your website you would want to implement some human verification to prevent getting spammed by bots.
In the code below we’ll see how to add the necessary code to the frontend and how to implement it with PHP in the backend.
Recaptcha SignUp
Note: Make sure you keep your private key secure. The recaptcha created with the keys in this tutorial was already deleted before this post went online so there is no security risk here.
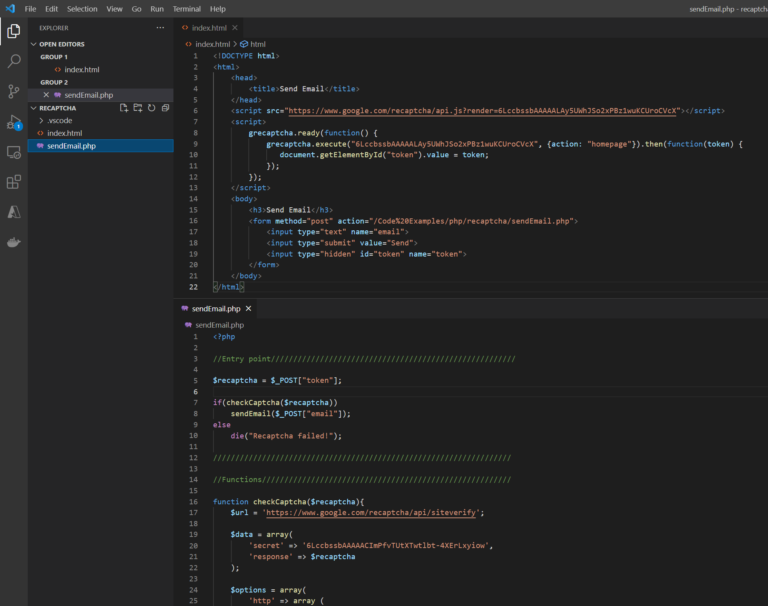
Code:
html
Replace the key in grcaptcha.execute(“”) and in the script src https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js?render= with your public key.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Send Email</title>
</head>
<script src="https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js?render=6LccbssbAAAAALAy5UWhJSo2xPBz1wuKCUroCVcX"></script>
<script>
grecaptcha.ready(function() {
grecaptcha.execute("6LccbssbAAAAALAy5UWhJSo2xPBz1wuKCUroCVcX", {action: "homepage"}).then(function(token) {
document.getElementById("token").value = token;
});
});
</script>
<body>
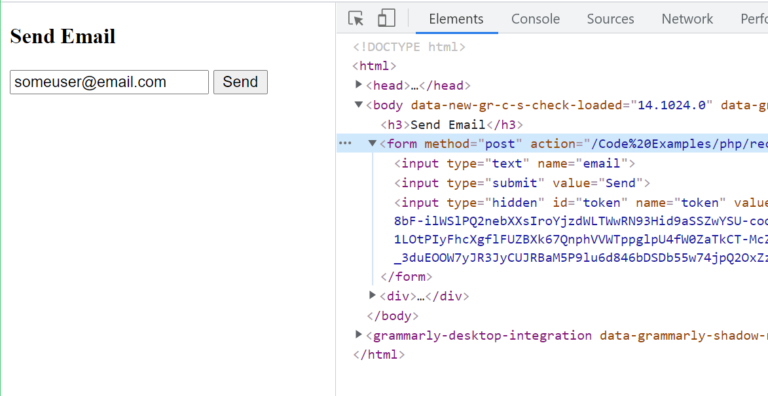
<h3>Send Email</h3>
<form method="post" action="/Code%20Examples/php/recaptcha/sendEmail.php">
<input type="text" name="email">
<input type="submit" value="Send">
<input type="hidden" id="token" name="token">
</form>
</body>
</html> PHP
In the data array replace the key for ‘secret’ with your private key.
<?php
//Entry point///////////////////////////////////////////////////////
$recaptcha = $_POST["token"];
if(checkCaptcha($recaptcha))
sendEmail($_POST["email"]);
else
die("Recaptcha failed!");
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//Functions////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
function checkCaptcha($recaptcha){
$url = 'https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify';
$data = array(
'secret' => '6LccbssbAAAAACImPfvTUtXTwtlbt-4XErLxyiow',
'response' => $recaptcha
);
$options = array(
'http' => array (
'header' => "Content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\r\n",
'method' => 'POST',
'content' => http_build_query($data)
)
);
$context = stream_context_create($options);
$verify = file_get_contents($url, false, $context);
$captcha_success = json_decode($verify);
return $captcha_success->success;
}
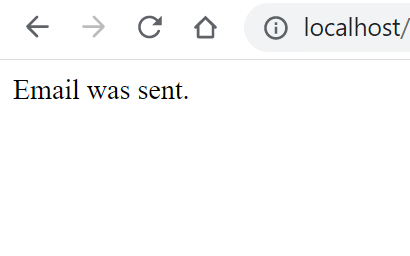
function sendEmail($email){
echo "Email was sent.";
//Not really... we would have to implement the code but you get the idea of this demo.
//If you would like to know how to send an emails with PHP check out this post I made:
//https://eecs.blog/php-sending-emails/
//Also check out this post on sanitizing your input data.
//https://eecs.blog/php-string-sanitization/
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Resulting output:

About
In this code snippet, we’ll learn how to perform string sanitization in PHP.
An attacker might try to inject some malicious code into your backend. As a developer, you can prevent that by filtering/sanitizing and validating your data before working with it.
Let’s see how to sanitize your strings in the example below.
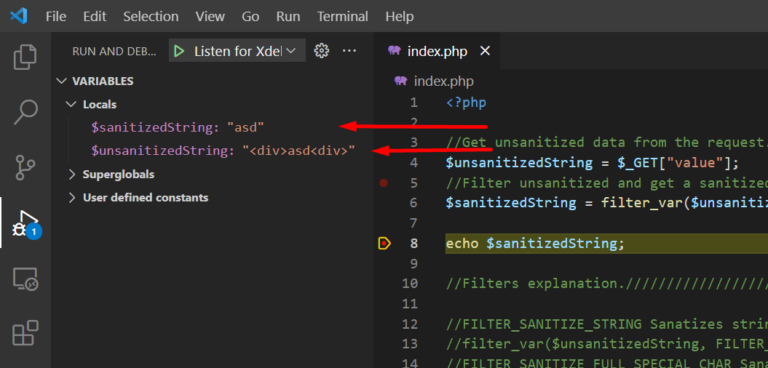
Code:
<?php //Get unsanitized data from the request. $unsanitizedString = $_GET["value"]; //Filter unsanitized and get a sanitized string. $sanitizedString = filter_var($unsanitizedString, FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING); echo $sanitizedString; //Filters explanation.//////////////////////////// //FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING Sanatizes string. //filter_var($unsanitizedString, FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING); //FILTER_SANITIZE_FULL_SPECIAL_CHAR Sanatizes string but encodes special characters instead of removing them. //filter_var($unsanitizedString, FILTER_SANITIZE_FULL_SPECIAL_CHARS); //FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL Sanatizes the string except the email. //filter_var($unsanitizedString, FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL); //More filters: https://www.php.net/manual/en/filter.filters.sanitize.php //////////////////////////////////////////////////