About
In this code snippet, we will take a look at string literals and the @ character in C#.
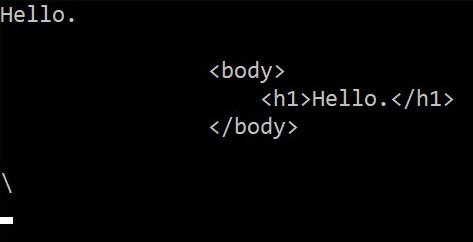
In C# the @ character can either be used to make reserved keywords available as variable names or it can be used to make a string literal. A string literal takes everything in the string literally. For example, you do not have to escape a \ with \\ . Your string can now also span multiple rows in the editor. This can be useful when making SQL statements or HTML, XML, …
Let’s have a look at the code below to see how to use the @ character.
Code:
using System;
namespace stringLiteral
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//1.
//If prefixed with @ reserved keywords can be used as variable names.
string @int = "Hello.";
Console.WriteLine(@int);
//2.1
//A string literal enables the string to span multiple rows.
string literal = @"
<body>
<h1>Hello.</h1>
</body>
";
Console.WriteLine(literal);
//2.2
//No need for escaping characters.
string literal2 = @"\";
Console.WriteLine(literal2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}