About
In this code snippet, we will take a look at lambda expressions, Func<T> and Action<T> in C#.
Func<T> is simply a more compact way of defining a delegate/function pointer while Action<T> is the exact same thing as Func<T> but for methods that return void.
The lambda operator () => is a more compact way to define an anonymous method that can then be assigned to a delegate or passed into another method as a parameter. It’s very often combined with LINQ to form very concise queries that all fit into a single line of code.
Let’s have a look at the code below to see how to use lambda expressions, Func<T> and Action<T>.
Code:
//Func<> is simply a more compact way of defining a delegate/function pointer.
//Func<return type, input param1, input param2, ...>
Func<double, double, double> operation = addition;
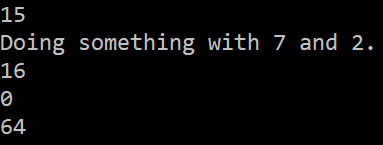
Calculate(operation, 10, 5);
//Action<> is the same as Func<> but is meant for methods that return void.
//Action<input param1, input param2, ...>
Action<int, int> myAction = MyTestVoidMethod;
myAction(7,2);
//The lambda operator () => is simply a more compact way of defining an anonymous method.
//It can be used in conjunction or as a more compact replacement for Action<> and Func<>.
Func<double, double, double> add = (a, b) => { return a + b; };
Calculate(add, 8, 8);
//Or an even more compact way.
Func<double, double, double> sub = (a, b) => a - b;
Calculate(sub, 8, 8);
//Or even more compact without Func<> or Action<>.
Calculate((a, b) => a * b, 8, 8);
Console.ReadLine();
static void MyTestVoidMethod(int input, int input2)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Doing something with {input} and {input2}.");
}
static void Calculate(Func<double, double, double> operation, double operand1, double operand2)
{
double result = operation(operand1, operand2);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static double addition(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
static double subtract(double a, double b)
{
return a - b;
}
static double multiply(double a, double b)
{
return a * b;
}
static double divide(double a, double b)
{
return a / b;
}