About
In this code snippet, we will take a look at operator overloading in C#.
Just like methods, operators can be overloaded too. In the code below we have an example with geometric shapes. If we use the + operator on two objects of GeomentricShapes we get an error. This happens because the compiler doesn’t know what is supposed to happen when the + operator is used on a GeomentricShapes object. We have to overload the + operator and write the code to be executed when two GeomentricShapes objects are added together.
Let’s look at the code example below to see how to overload operators.
Code:
using System;
namespace OperatorOverloading
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Square square1 = new Square(15, 20);
Square square2 = new Square(33, 8);
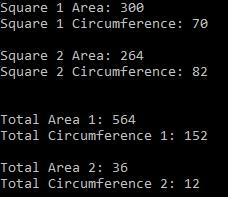
Console.WriteLine("Square 1 Area: " + square1.Area);
Console.WriteLine("Square 1 Circumference: " + square1.Circumference);
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("Square 2 Area: " + square2.Area);
Console.WriteLine("Square 2 Circumference: " + square2.Circumference);
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("");
GeometricShapes geoShape = square1 + square2;
Console.WriteLine("Total Area 1: " + geoShape.Area);
Console.WriteLine("Total Circumference 1: " + geoShape.Circumference);
Console.WriteLine("");
GeometricShapes geoShape2 = square1 - square2;
Console.WriteLine("Total Area 2: " + geoShape2.Area);
Console.WriteLine("Total Circumference 2: " + geoShape2.Circumference);
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class GeometricShapes
{
public double Area { get; set; }
public double Circumference { get; set; }
public GeometricShapes()
{
}
public GeometricShapes(double area, double circumference)
{
this.Area = area;
this.Circumference = circumference;
}
//Operator overloading.
public static GeometricShapes operator +(GeometricShapes shape1, GeometricShapes shape2)
{
//Here we define what happens when the + operator will be used on a GeometricShapes instance.
return new GeometricShapes((shape1.Area + shape2.Area), (shape1.Circumference + shape2.Circumference));
}
public static GeometricShapes operator -(GeometricShapes shape1, GeometricShapes shape2)
{
//Here we define what happens when the - operator will be used on a GeometricShapes instance.
return new GeometricShapes(Math.Abs(shape1.Area - shape2.Area), Math.Abs(shape1.Circumference - shape2.Circumference));
}
}
class Square : GeometricShapes
{
public double SideA { get; set; }
public double SideB { get; set; }
public Square(double sideA, double sideB)
{
this.SideA = sideA;
this.SideB = SideB;
this.Area = sideA * sideB;
this.Circumference = (sideA * 2) + (sideB * 2);
}
}
}