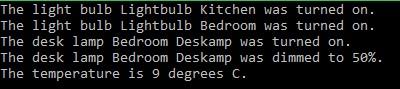
About
In this code snippet, we will take a look at interfaces in C#.
When I was first learning about interfaces I was given this analogy: “Interfaces are like contracts that specify what a class has to implement”. When a class uses an interface it must implement everything that the interface specifies.
Interfaces are very similar to abstract classes. But a class can only inherit from one other class meanwhile it can implement multiple interfaces. When naming an interface the convention is to start the name with I.
Interfaces can contain: events, indexers, methods, properties
Interfaces can’t contain: constants, types, fields, constructors, operators, finalizers
Let’s have a look at the code below to see how to make an interface.
Code:
using System;
namespace Interfaces
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//In this example we we will make objects of IOT(internet of things) devices.
LightBulb bulb1 = new LightBulb("Lightbulb Kitchen", "192.168.1.10");
LightBulb bulb2 = new LightBulb("Lightbulb Bedroom", "192.168.1.11");
DeskLamp lamp1 = new DeskLamp("Bedroom Deskamp", "192.168.1.12");
TemperatureSensor temp1 = new TemperatureSensor("Temperature Sensor Yard", "192.168.1.13");
bulb1.on();
bulb2.on();
lamp1.on();
lamp1.dimm(50);
temp1.getTemperature();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
/******************************************** Interfaces **********************************************/
//Interfaces contain the things that must be implemented when that particular interface is used.
//Each class using the interface can define a different implementation for a particular member of the interface.
//For example the on() method is implemented a bit differntly for every device.
//Every IOT device should implement this interface.
interface IOTDevice
{
string Name { get; set; }
string IpAdress { get; set; }
}
//Some devices are controllable(can be turned on/off). Those should implement this interface.
interface IControllable
{
void on();
void off();
}
//Some lights are dimmable. Those should implement this interface.
interface IDimmable
{
void dimm(int percent);
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//As you see a class can implement multiple interfaces.
class LightBulb : IOTDevice, IDimmable, IControllable // <= Interfaces
{
public LightBulb(string name, string ipAdress)
{
Name = name;
IpAdress = ipAdress;
}
//IOTDevice interface implementation ////////////////////
public string Name { get; set; }
public string IpAdress { get; set; }
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//IControllable interface implementation ////////////////
public void off()
{
Console.WriteLine("The light bulb " + Name + " was turned off.");
}
public void on()
{
Console.WriteLine("The light bulb " + Name + " was turned on.");
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//IDimmable interface implementation ////////////////////
public void dimm(int percent)
{
Console.WriteLine("The light bulb " + Name + " was dimmed to " + percent + "%.");
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
}
class DeskLamp : IOTDevice, IDimmable, IControllable
{
public DeskLamp(string name, string ipAdress)
{
Name = name;
IpAdress = ipAdress;
}
//IOTDevice interface implementation ////////////////////
public string Name { get; set; }
public string IpAdress { get; set; }
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//IControllable interface implementation ////////////////
public void off()
{
Console.WriteLine("The desk lamp " + Name + " was turned off.");
}
public void on()
{
Console.WriteLine("The desk lamp " + Name + " was turned on.");
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//IDimmable interface implementation ////////////////////
public void dimm(int percent)
{
Console.WriteLine("The desk lamp " + Name + " was dimmed to " + percent + "%.");
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
}
class TemperatureSensor : IOTDevice
{
public TemperatureSensor(string name, string ipAdress)
{
Name = name;
IpAdress = ipAdress;
}
//IOTDevice interface implementation ////////////////////
public string Name { get; set; }
public string IpAdress { get; set; }
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public void getTemperature()
{
//Yeah ... not really getting the temperature here, just making up some random numbers.
Random rand = new Random();
Console.WriteLine("The temperature is " + rand.Next(-20, 40) + " degrees C.");
}
}
}