About
In this code snippet, we will learn about JSON serialization in C#.
Serialization is when you take an object and convert it to a stream of bytes that can be then stored in a file, database or memory. This is useful if you want to store the state of your objects or send them over the network(for example an API). Of course, you can also deserialize a file/database entry back into an object.
Note: See also XML and binary serialization.
In this example, we will serialize and deserialize an object to/from JSON. I will only make a JSON string. To make a JSON file you simply write the string to the file like you would for any other text. At the end just make sure to save the file with the .json extension instead of .txt.
Let’s have a look at the code below to see how to perform JSON serialization.
Code:
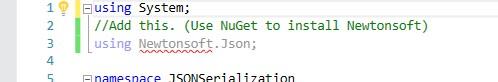
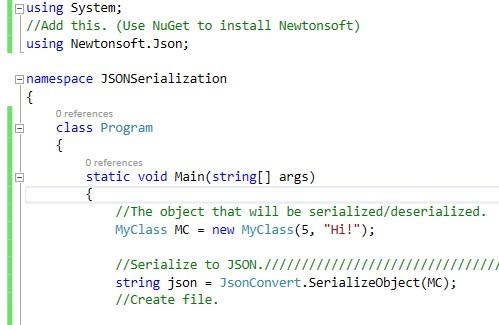
using System;
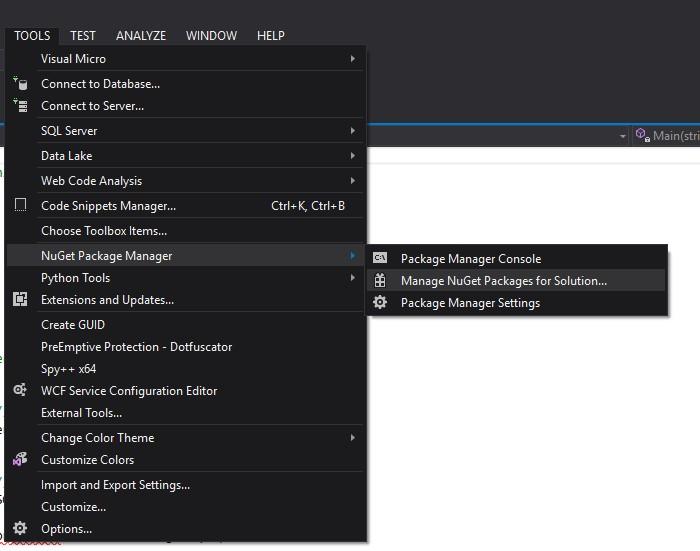
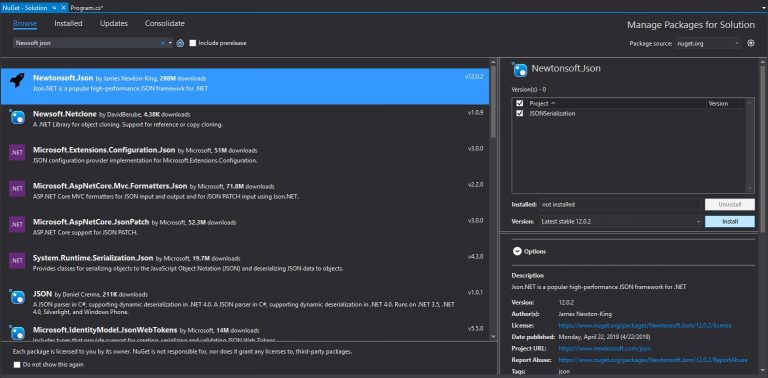
//Add this. (Use NuGet to install Newtonsoft library)
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace JSONSerialization
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//The object that will be serialized/deserialized.
MyClass MC = new MyClass(5, "Hi!");
//Serialize to JSON.////////////////////////////////////////////////
string json = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(MC);
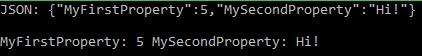
Console.WriteLine("JSON: " + json);
Console.WriteLine();
//Deserialize from JSON.///////////////////////////////////////////
MyClass MCDeserializedFromJSON = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<MyClass>(json);
Console.WriteLine("MyFirstProperty: " + MCDeserializedFromJSON.MyFirstProperty + " MySecondProperty: " + MCDeserializedFromJSON.MySecondProperty);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
//Make sure the class that will be serailized is public.
//Also all the members of the class that will be serialized must be public.
public class MyClass
{
public int MyFirstProperty { get; set; }
public string MySecondProperty { get; set; }
public MyClass()
{
}
public MyClass(int a, string b)
{
MyFirstProperty = a;
MySecondProperty = b;
}
}
}